vue3中的watch详细讲解保证看的明明白白

Vue3 中的 watch 只能监视以下四种数据
1,ref 定义的数据。
2,一个响应式对象(如:reactive 定义的数据)。
3,函数的返回一个值(getter函数)。getter函数其实就是:能返回一个值的函数
4,由以上类型的值组成的数组
地址:https://cn.vuejs.org/api/reactivity-core.html#watch

vue3中watch监听 ref定义的基本数据类型
<template> <div class="box"> 姓 <input v-model="xingValue" /> <br> <button @click="changeHandler">更改值</button> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref, computed, watch } from 'vue'; const xingValue = ref('Zhang'); function changeHandler(){ xingValue.value = 'Li'; } watch(xingValue, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('watch监听到的值新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) }) </script> 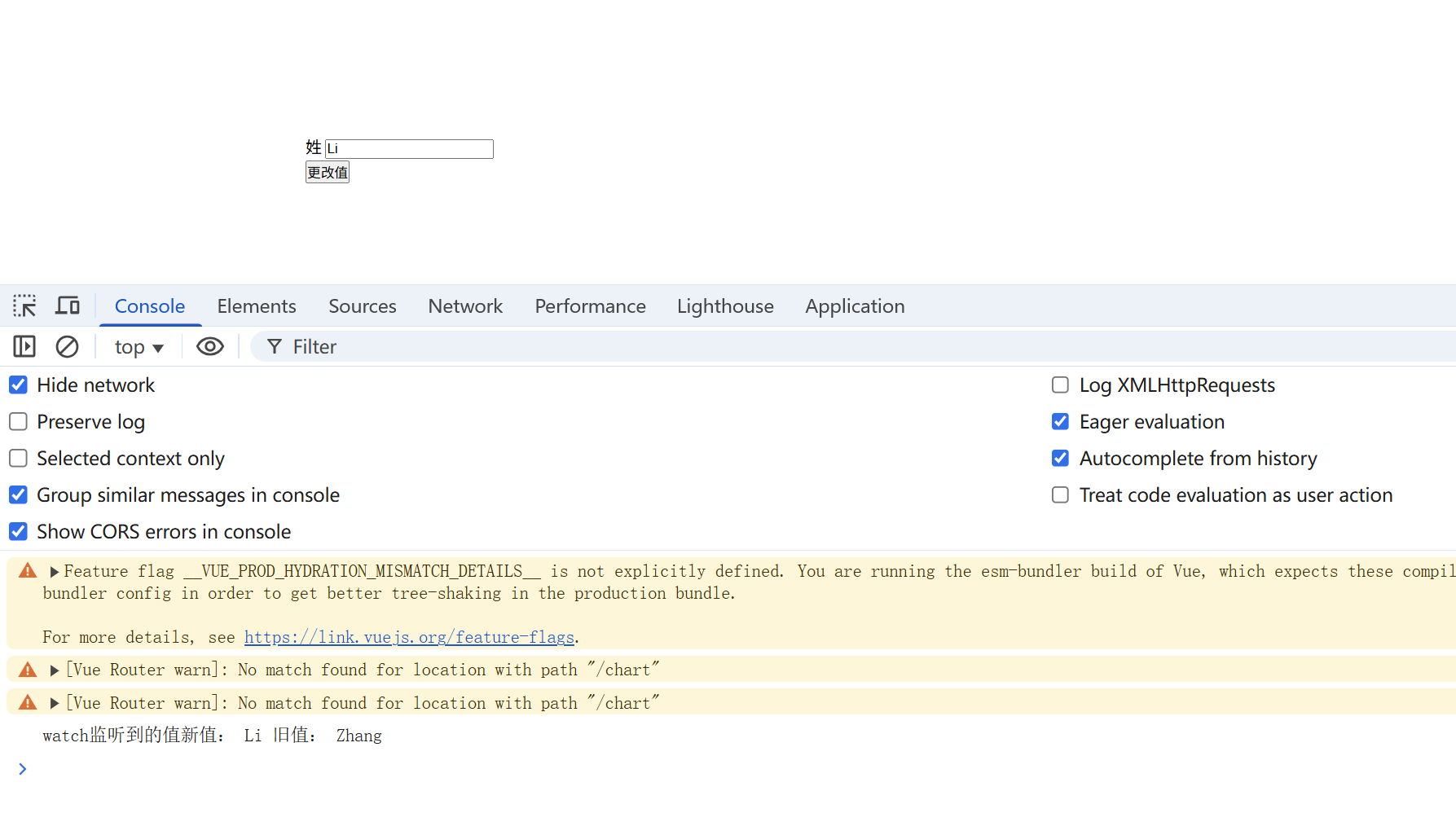
watch监听ref声明的数据,第1个参数是不需要点value
如果我们使用watch监听ref声明的数据,第1个参数是不需要点value的。
const age = ref(1); // watch监听ref声明的数据,第1个参数是不需要点value watch(age, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('watch监听到的值新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) }) 如果你使用ref声明的数据,如果你使用了点value。那么会报错的哈。
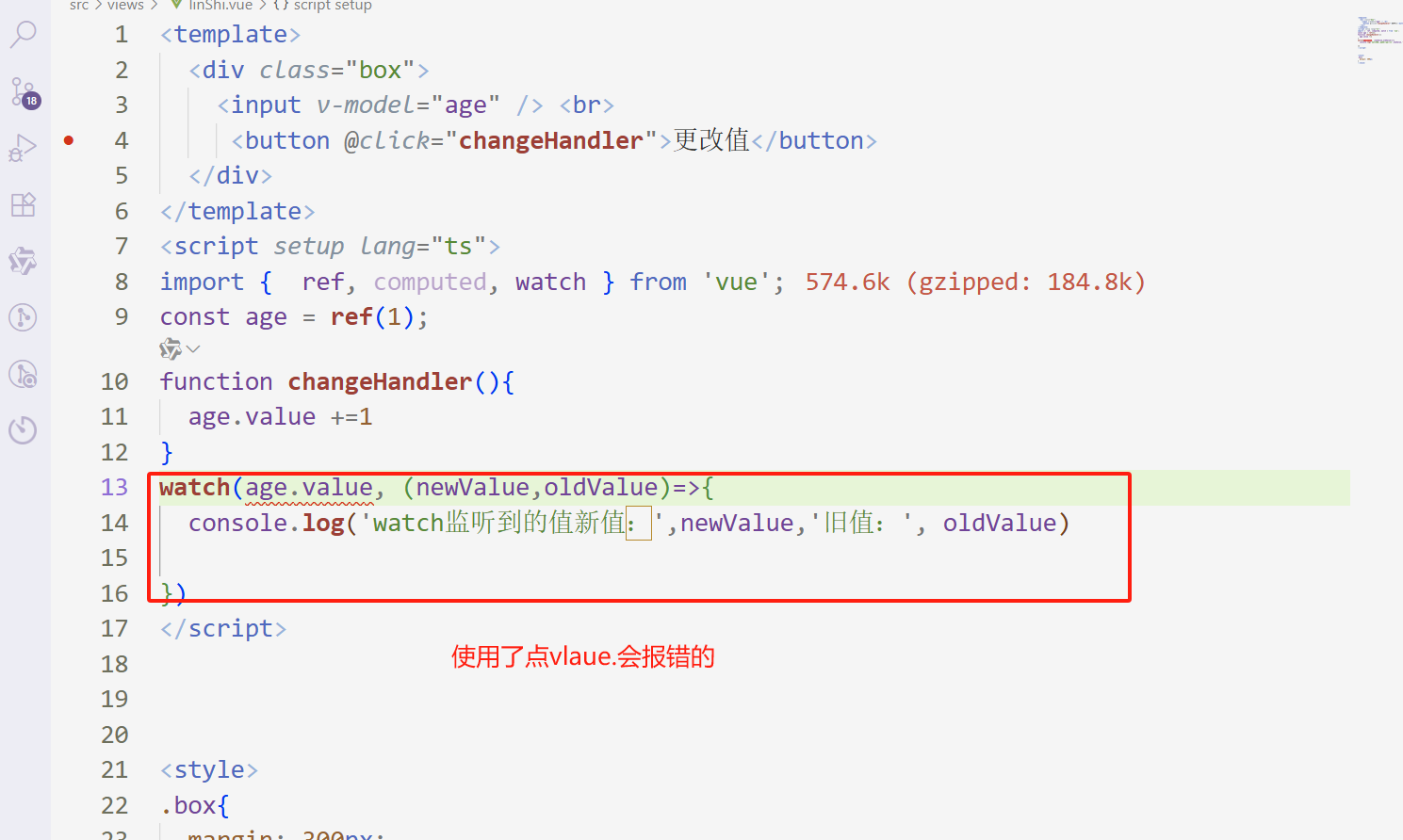
watch监听ref定义的对象数据类型
watch监听ref定义的【对象】数据类型时,监听的是对象的地址。
若是想要监听【对象内部属】性的变化,也就是细枝末节的变化。首要手动开启deep:true。
若是不开启deep:true,则监听不到。
watch监听ref定义的【对象】数据类型时,若是不开启deep:true,则监听不到对象内部属性的变化。
<template> <div class="box"> <p>{{ perosn }}</p> <button @click="changeHandler">更改值</button> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref, computed, watch } from 'vue'; const perosn = ref({ name: 'zhangsan', age: 18 }); function changeHandler(){ perosn.value.age+=1 } watch(perosn, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('watch监听到的值新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) }) </script> 为啥更改ref定义的【对象】的属性时不会触发。
因为:watch监听ref定义的【对象】数据类型时,监听的是对象的地址。
地址没有发生改变,因此就不会触发。
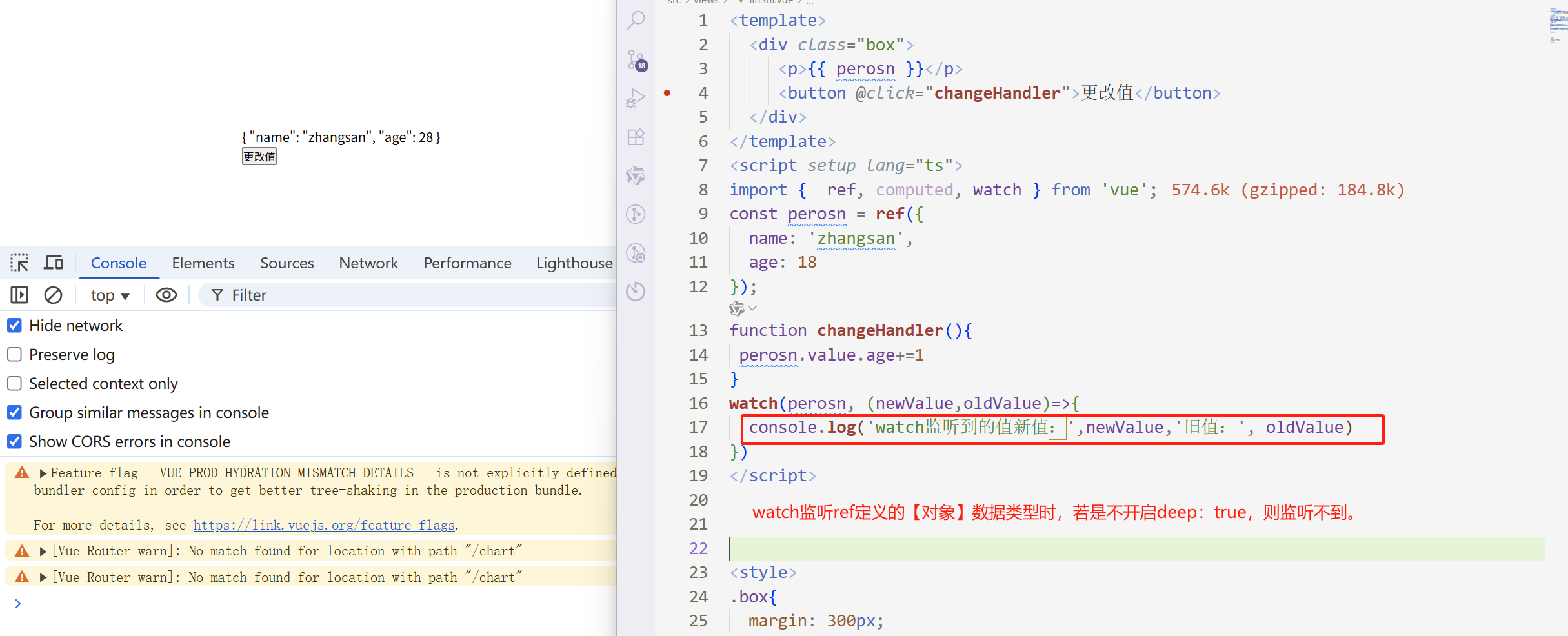
如果想要:地址不发生改变时,也触发 ,需要开启:deep:true
watch开启deep:true监听ref对象内部属性的变化
watch开启deep:true监听ref对象内部属性的变化
<template> <div class="box"> <p>{{ perosn }}</p> <button @click="changeHandler">更改值</button> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref, computed, watch } from 'vue'; const perosn = ref({ name: 'zhangsan', age: 18 }); function changeHandler(){ perosn.value.age+=1 } watch(perosn, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('watch监听到的值新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) },{ deep: true }) </script> 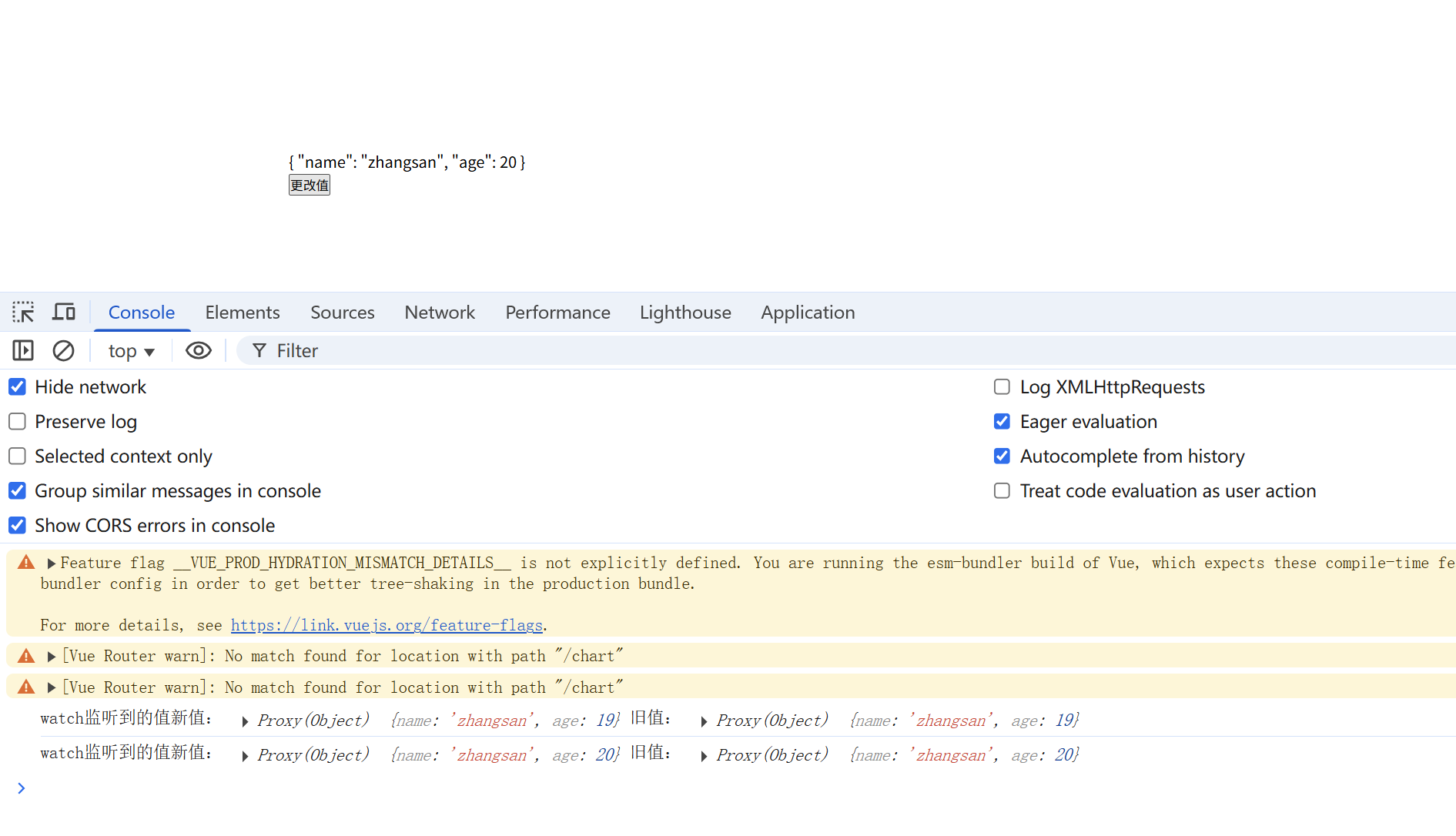
watch监听ref定义的对象内部属性变化时,开启deep:true 新值和旧值是一样的

因为:watch监听ref定义的【对象】数据类型时,监听的是对象的地址。他们的地址是没有发生改变的。
watch监听ref定义的对象时,修改整个对象,newValue 和 oldValue 是不一样的
<template> <div class="box"> <p>{{ perosn }}</p> <button @click="allHandler">更改整个属性</button> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref, computed, watch } from 'vue'; const perosn = ref({ name: 'zhangsan', age: 18 }); function allHandler(){ // 若修改整个ref 定义的对象,这个时候地址发生变化了。 // 如果你多次点击,会多次触发。 perosn.value = { name: 'wangmazi', age: 30 } } watch(perosn, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) },{ deep: true }) </script> 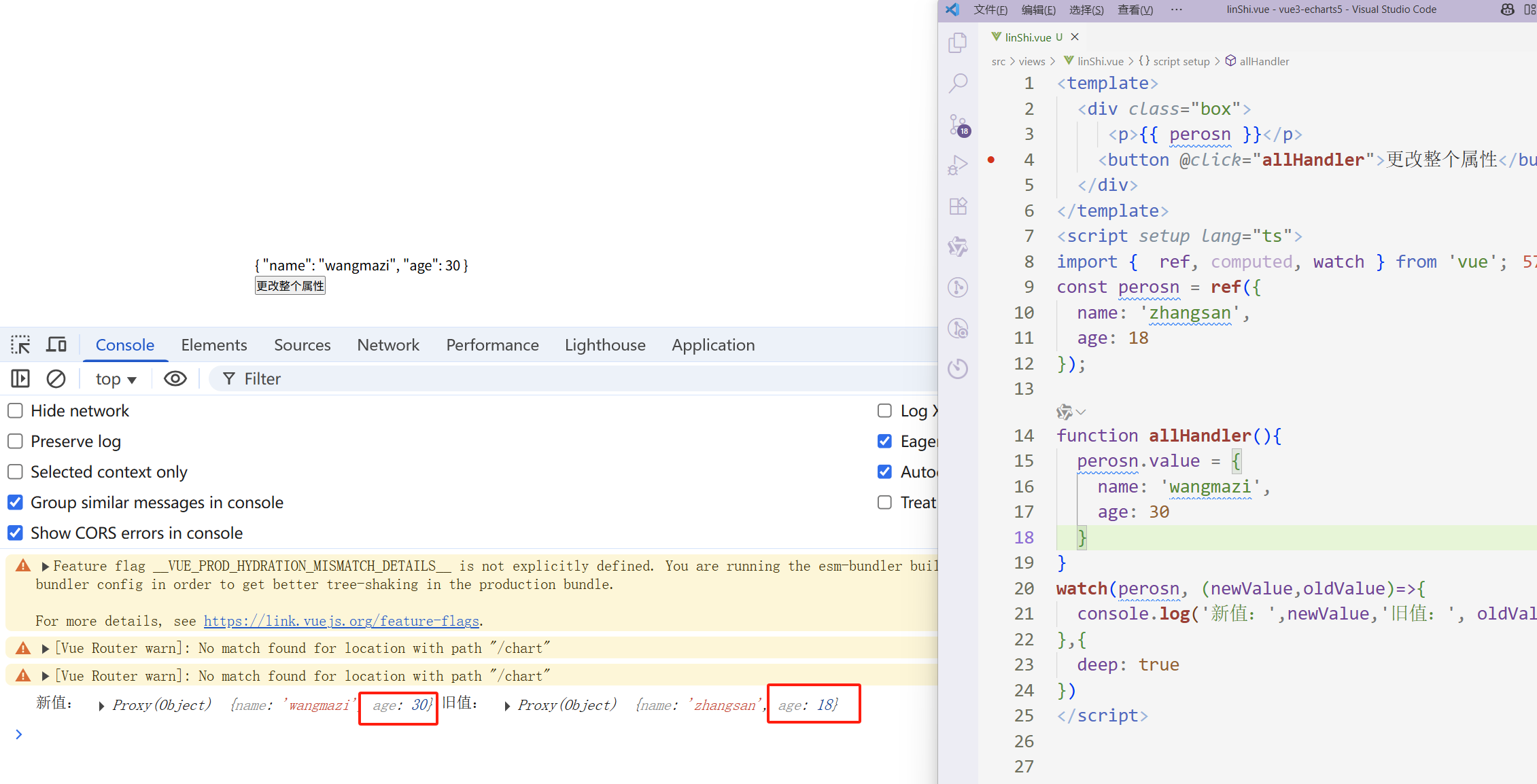
总结:watch监听ref声明对象类型的数据时
watch监视 ref 定义的【对象类型】数据时,直接写数据名,监视的是对象的【地址值】
若想监视对象内部的数据,要手动开启深度监视
若修改的是 ref 定义的对象中的属性,newValue 和 oldValue 都是新值,因为它们是同一个对象。
若修改整个ref 定义的对象,newValue 是新值, oldValue 是旧值,因为不是同一个对象了
watch监视【reactive】定义的【对象类型数据】,默认是开启深度监视的
只要我们使用watch去监听reactive定义的对象类型数据
无论数据层级有多么深,watch都是可以监听到的,并且它默认是开启了深度监听的。
无论内部变化的是某个属性,还是对象,都可以监听到。
监听这种是最省心的,因为无论怎么变化,都是可以监听到的哈哈。
<template> <div> <h1>{{ person }}</h1> <button @click="allHandler">更改car这个对象</button> <button @click="oneNameHandler">更改某个属性name</button> </div> </template> <script lang="ts" setup> import { watch,reactive } from 'vue'; const person = reactive({ age:18, name:'张三', car:{ c1:'电动车', c2:'燃油车' } }); function allHandler(){ person.car = { c1:'小米', c2:'Su7' } } function oneNameHandler(){ person.name = '李四'; } // watch监视【reactive】定义的【对象类型数据】,默认是开启深度监视的 // 无论内部变化的是某个属性,还是对象,都可以监听到。 watch(person, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue) console.log('旧值:', oldValue) }) </script> 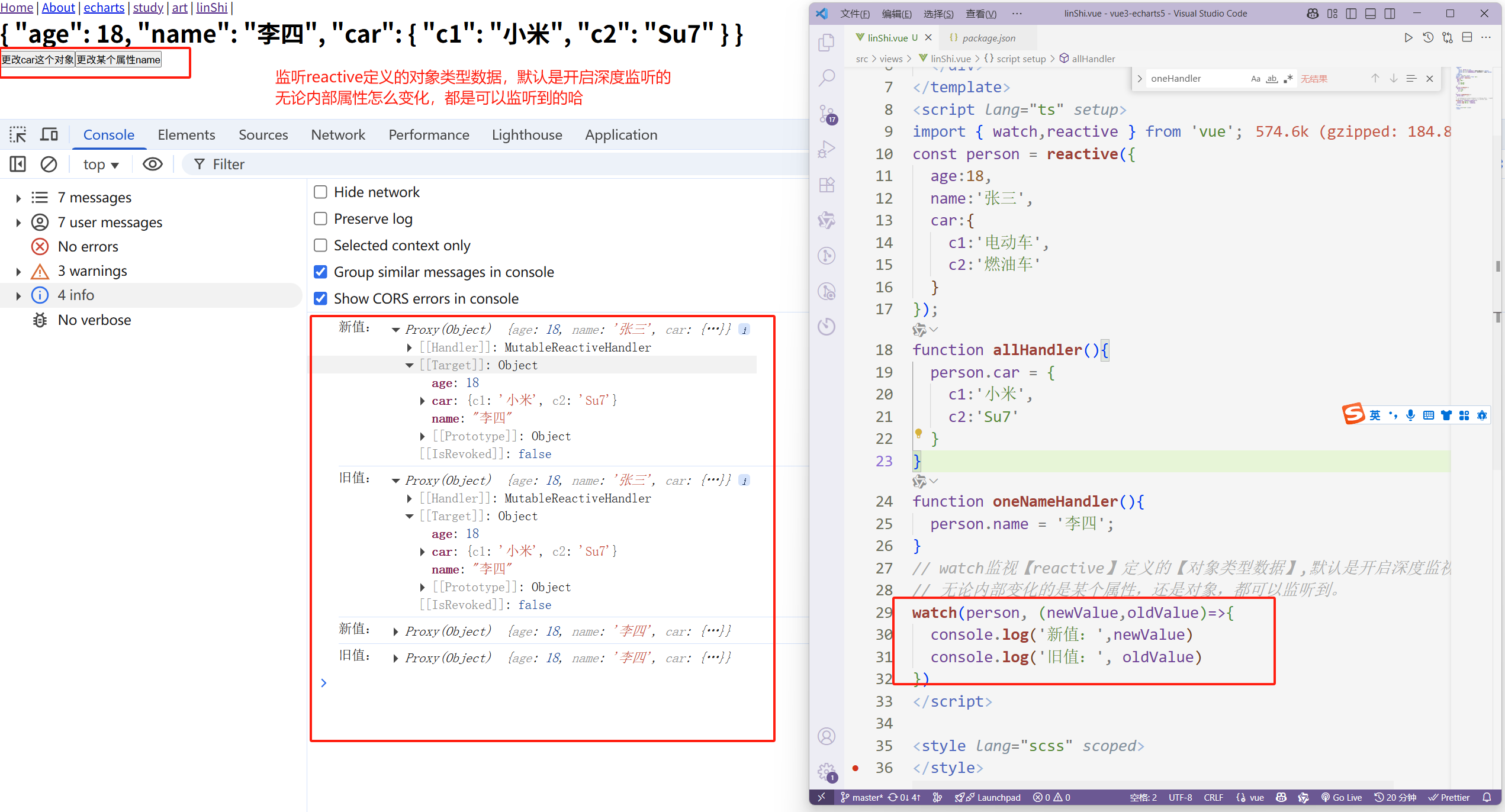
有的文章会说:这种深度监听你是无法通过deep:false来进行关闭的。
这种说法不太正确,在现在的vue3.5版本中。
通过deep:false是可以关闭监听的。
<template> <div class="box"> <p>{{ person }}</p> <button @click="allHandler">更改整个属性</button> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref, computed, watch, reactive } from 'vue'; const person = reactive({ a:{ b:{ c: 1 } } }); function allHandler(){ person.a.b.c +=1 } watch(person, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) },{ deep: false, }) </script> 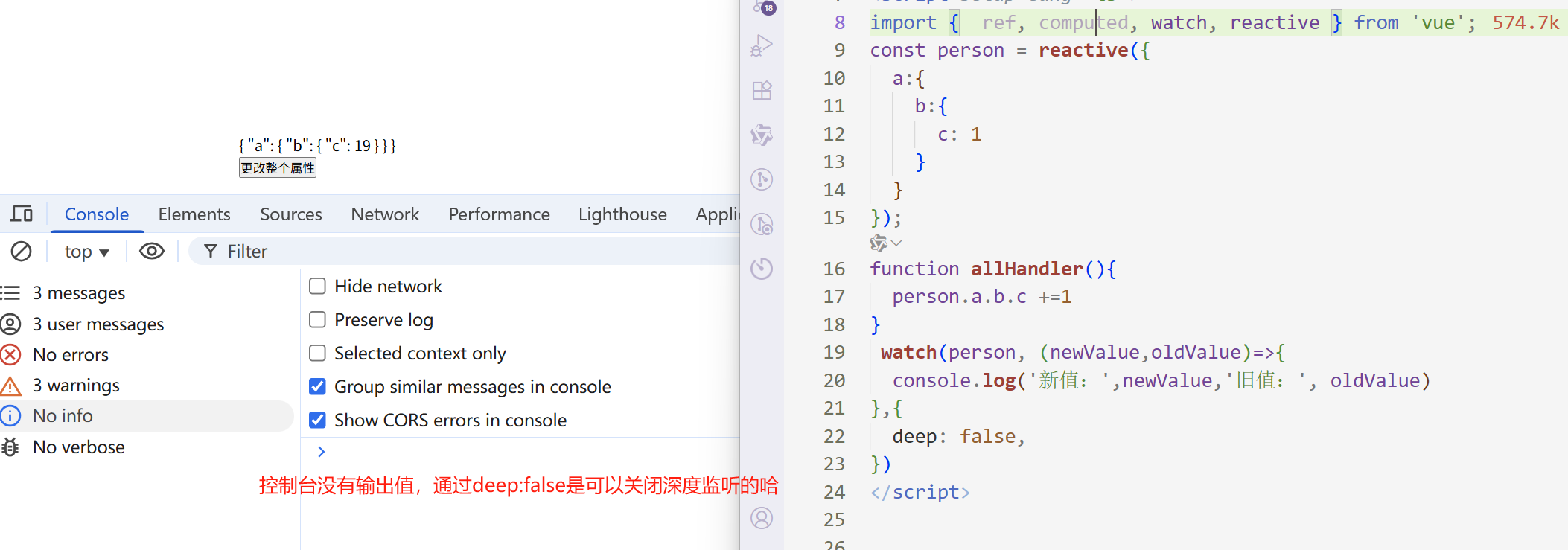
watch监视 ref 或 reactive定义的【对象类型】数据中的某个属性
watch监视 ref 或 reactive定义的【对象类型】数据中的某个属性,注意点如下:
1,若该属性值是【对象类型】,可直接写数据源,也可写成函数(建议写成函数)。并且推荐开启深度监听。
2,若该属性值不是【对象类型】,需要写成函数形式。否则会在控制台产生告警。
若该属性值不是【对象类型】,需要写成函数形式
<template> <div class="box"> <p>{{ person }}</p> <button @click="allHandler">更改整个属性</button> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref, computed, watch, reactive } from 'vue'; const person = reactive({ age:18, name:'张三', car:{ c1:'电动车', c2:'燃油车' } }); function allHandler(){ person.age+=1 } // 监听person.age属性,会产生警告。 watch(person.age, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) }) </script> 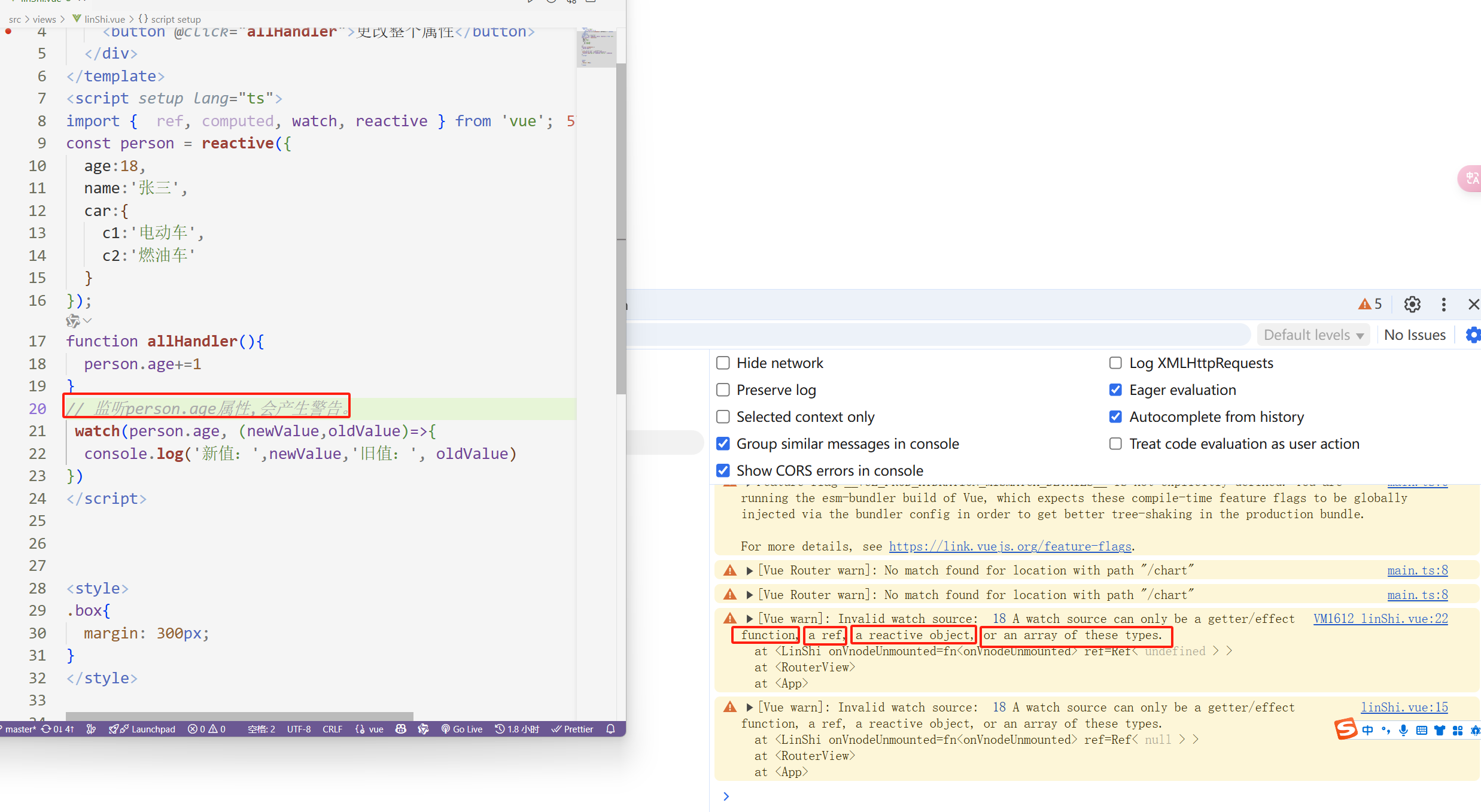
const person = ref({ age:18, name:'张三', car:{ c1:'电动车', c2:'燃油车' } }); watch(person.value.name, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('newValue', newValue) console.log('oldValue', oldValue) }) 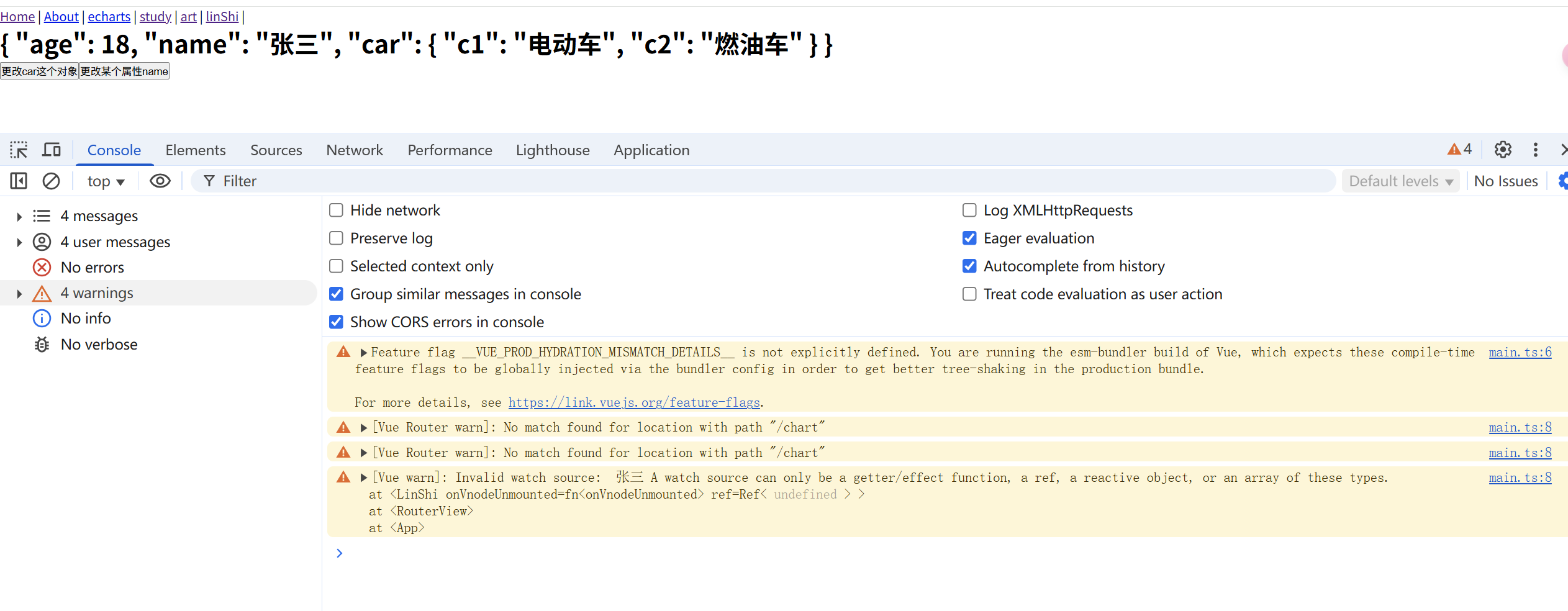
现在有警告。为啥会警告。
因为:watch监视 ref 或 reactive定义的【对象类型】数据中的某个属性时。
如果这个属性值不是对象类型时,需要写成函数形式。【重点】
// 因为这个属性值不是对象类型时,所以写成了函数形式 watch(()=> person.age, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) }) 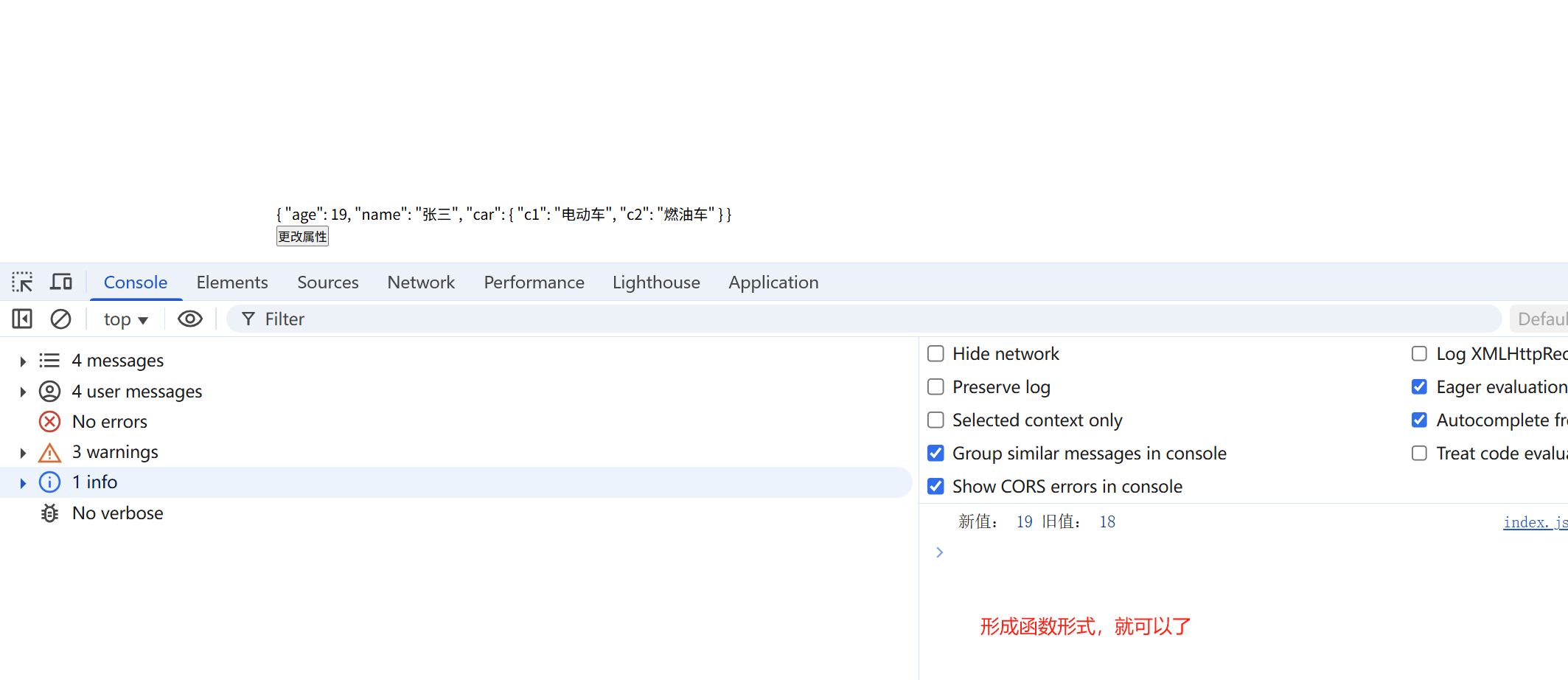
watch监听reactive定义的对象,监听的属性是对象(写成数据源形式),你替换整个对象,监听不到。
<template> <div class="box"> <p>{{ person }}</p> <button @click="allOneHandler">更改某个属性</button> <button @click="allHandler">更改整个对象</button> </div> </template> <script setup lang="ts"> import { ref, computed, watch, reactive } from 'vue'; const person = reactive({ age:18, name:'张三', car:{ c1:'电动车', c2:'燃油车' } }); function allOneHandler(){ person.car.c1 = '--我的电动车--'; } function allHandler(){ person.car = { c1:'--电动车--', c2:'--燃油车--' } } watch(person.car, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) }) </script> 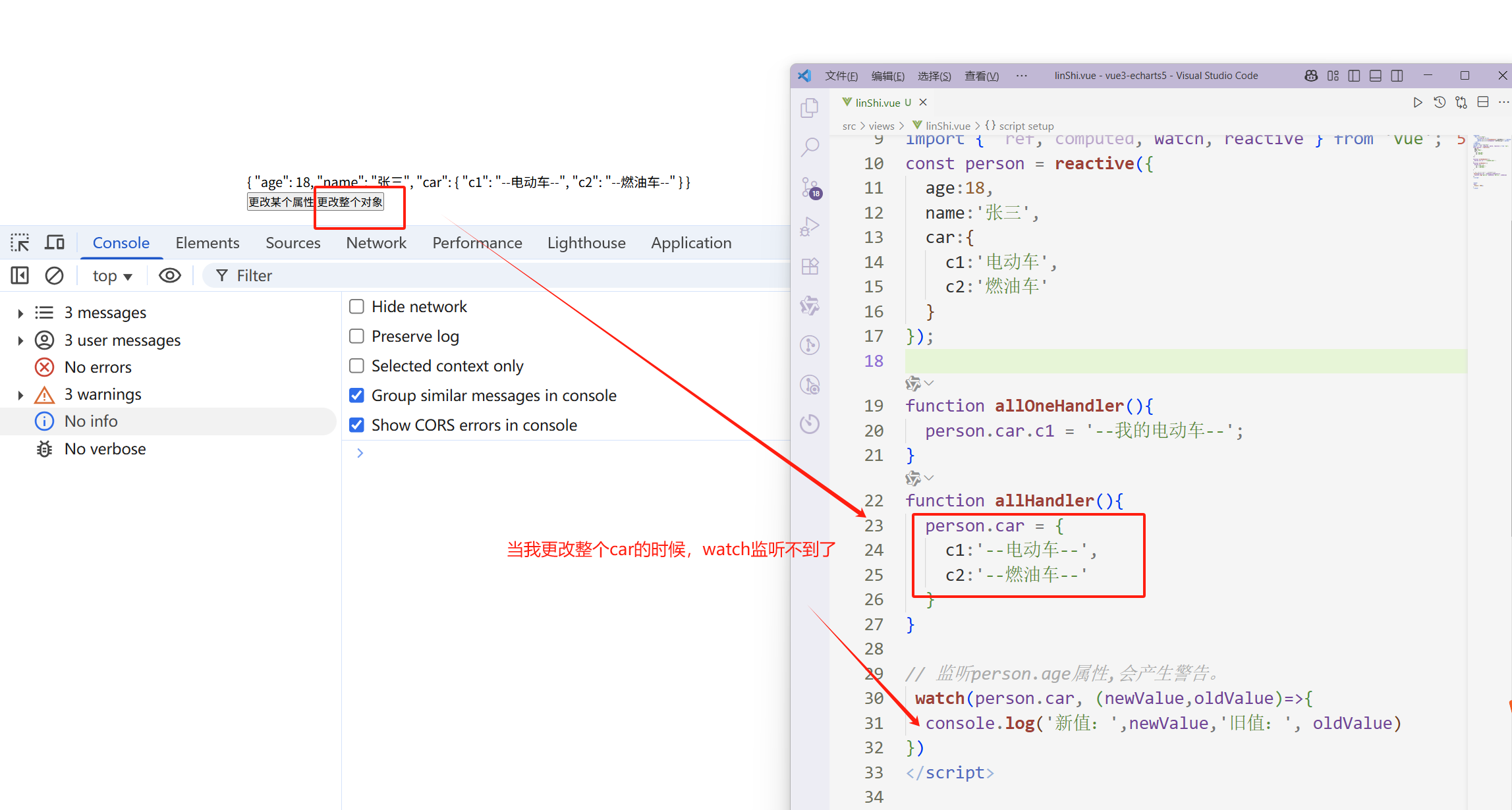
为什么上面的直接更改整个监听对象,监听不到。
person.car = { c1:'--电动车--', c2:'--燃油车--' } watch(person.car,()=>{}) 因为:当你替换整个car的时候,已经不再是原来的car。因此无法监听到。
怎么让它也可以监听到呢?写成函数形式。
const person = reactive({ age:18, name:'张三', car:{ c1:'电动车', c2:'燃油车' } }); function allHandler(){ person.car = { c1:'--电动车--', c2:'--燃油车--' } } watch(()=>person.car, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) }) 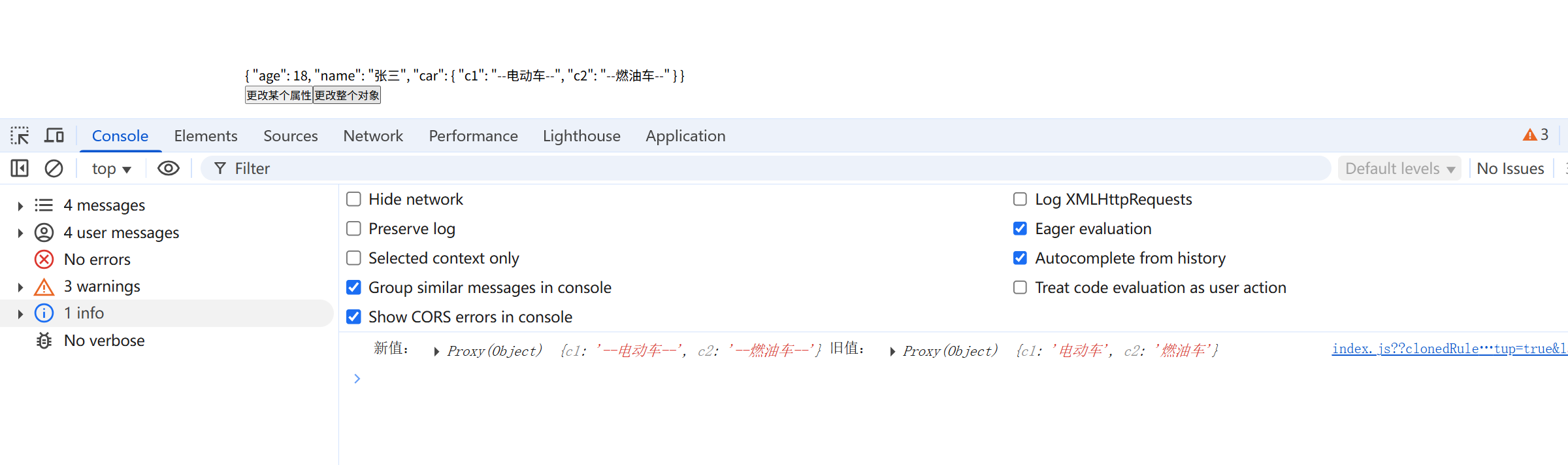
写成函数形式,监听整某个具体属性又不行了。
<template> <div> <h1>{{ person }}</h1> <button @click="allHandler">更改car这个对象</button> <button @click="allOneHandler">更改某个属性</button> </div> </template> <script lang="ts" setup> import { watch,reactive } from 'vue'; const person = reactive({ age:18, name:'张三', car:{ c1:'电动车', c2:'燃油车' } }); function allHandler(){ person.car = { c1:'--电动车--', c2:'--燃油车--' } } function allOneHandler(){ person.car.c1 += '--我的电动车--'; } watch(()=>person.car, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) }) </script> 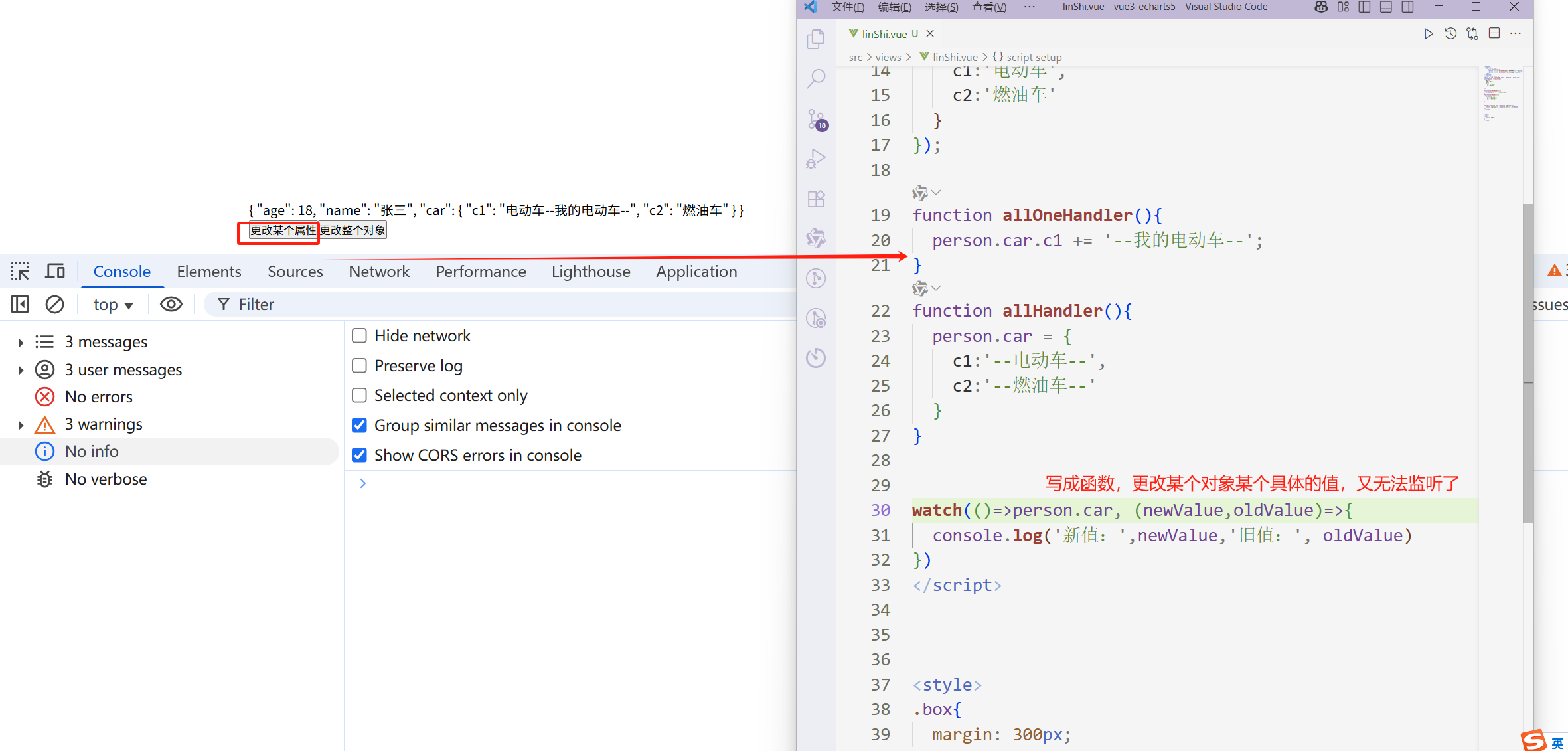
终极的解决办法
const person = reactive({ age:18, name:'张三', car:{ c1:'电动车', c2:'燃油车' } }); function allOneHandler(){ person.car.c1 += '--我的电动车--'; } function allHandler(){ person.car = { c1:'--电动车--', c2:'--燃油车--' } } watch(()=>person.car, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) },{ deep: true }) 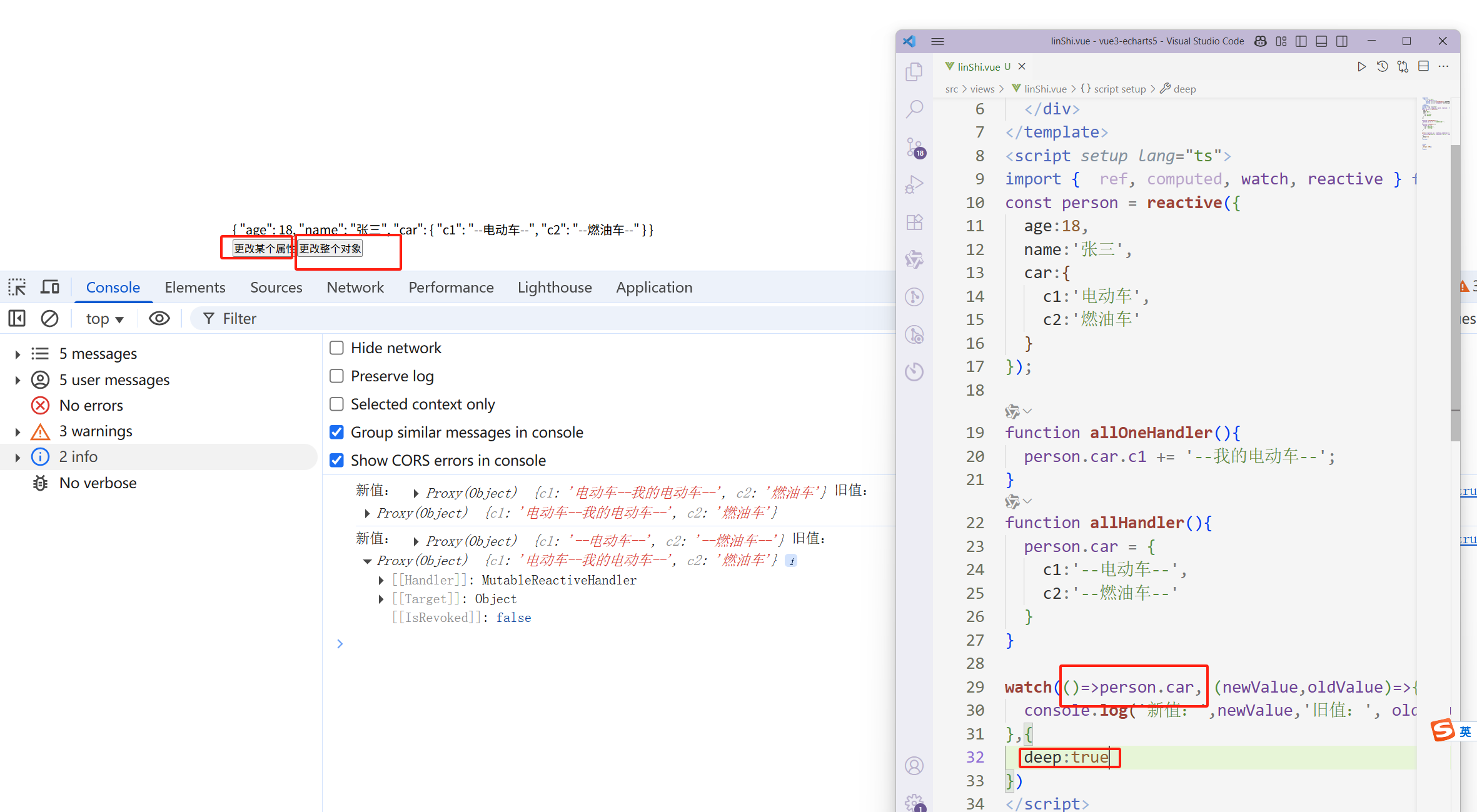
这样无论是更改整个对象还是对象内部的属性变化。都可以监听到啦。
总结:watch监听reactive/ref定义的内部属性时,监听的属性是对象,推荐写成函数形式,并且开启深度监听。
watch的数据源写成一个数组
有些时候,我们需要监听一个对象中的几个属性或者好几个不同的对象。
这个时候我们可以写成一个数组的形式
<template> <div> <h1>{{ person }}</h1> <button @click="allHandler">更改car这个对象</button> <button @click="oneNameHandler">更改某个属性name</button> </div> </template> <script lang="ts" setup> import { watch, reactive } from 'vue'; const person = reactive({ age:18, name:'张三', car:{ c1:'电动车', c2:'燃油车' } }); function allHandler(){ person.car = { c1:'小米Su7', c2:'小米Yu7' } } function oneNameHandler(){ person.name = '李四'; } watch(()=>[person.name, person.car.c1], (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('newValue', newValue) console.log('oldValue', oldValue) },{ deep:true }) </script> 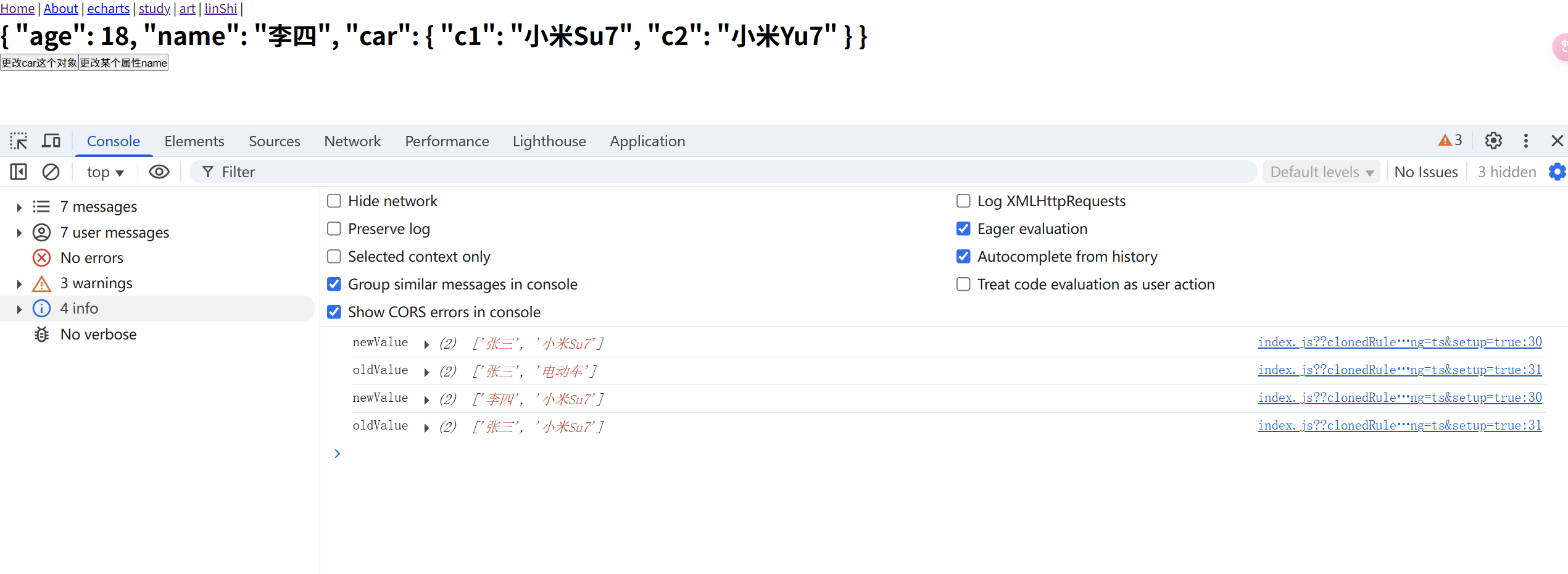
什么时候需要深度监听?
明明人家监听的是地址的变化,结果你想要监听某个值的变化
再次说明:watch为啥新值和旧值一样?
因为监听的是地址,你更改属性时,地址没有发生变化。
Object.assign更改时,也是只更改了属性,并没有产生新的地址。
相当于你新装修房子,你只换了灯,床,房子的地址没有发生变化。
因此:新值和旧值是一样的。
取消watch监听
将watch赋值给一个变量,调用这个变量。就可以停止监听了。
import { ref, computed, watch } from 'vue'; const age = ref(1); function changeHandler(){ age.value +=1 } let stopWatch = watch(age, (newValue,oldValue)=>{ console.log('watch监听到的值新值:',newValue,'旧值:', oldValue) if(newValue>3){ stopWatch() } }) </script> 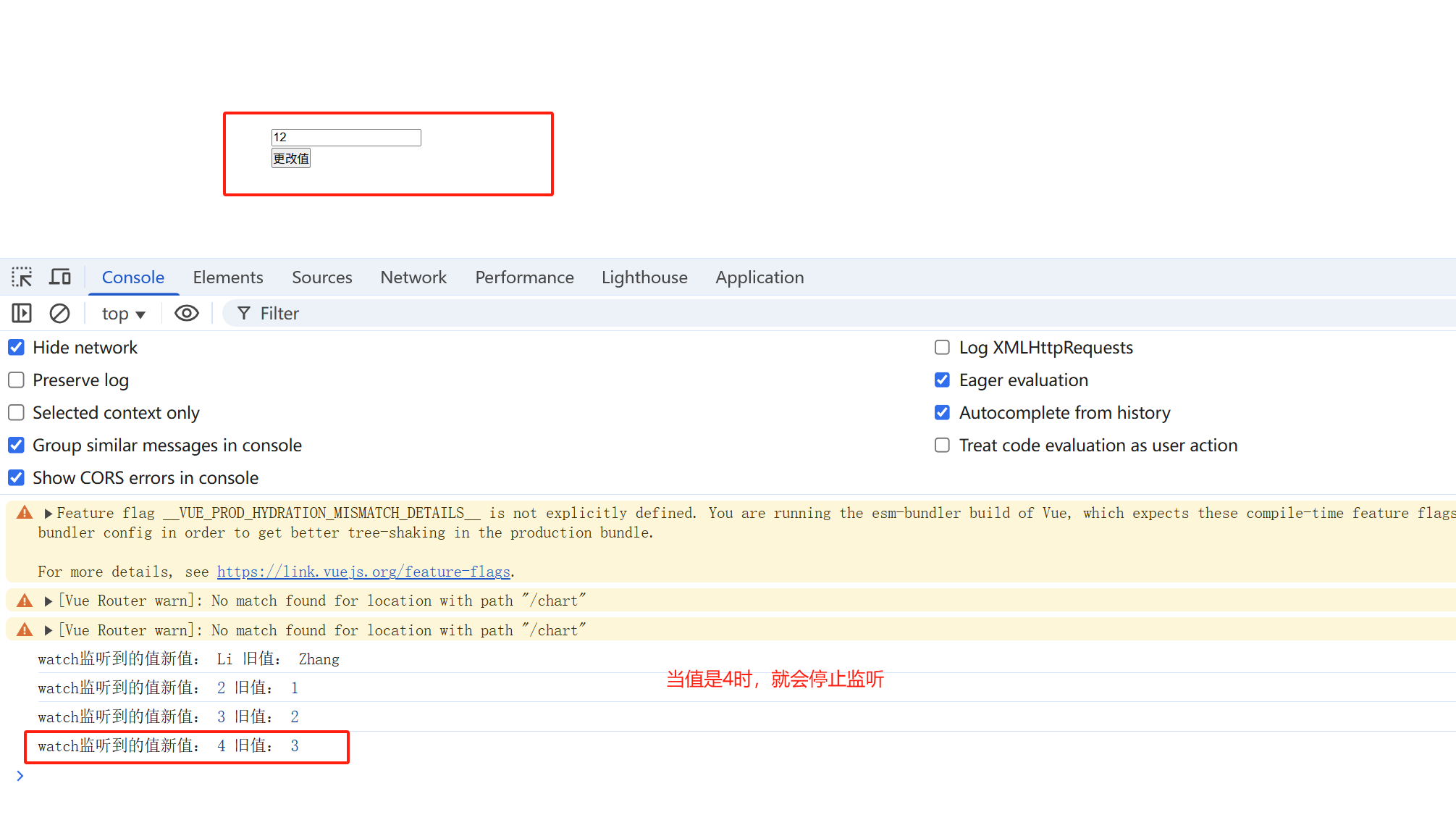









评论